Got big plans for 2020?
Want to take your business global, across continents and oceans?
That’s an ambitious plan.
However, it is destined to fail if you don’t speak the language that your foreign audience loves to hear.
A study posted in CSA research has shown that foreign audiences prefer to communicate with businesses in their native tongue. Reportedly:
- 60% of consumers rarely or never make purchases from websites that are only in English
- 67% prefer a site to have content and navigation in their native language
- 75% of consumers want to make purchases in their native language
Obviously, if a customer wants to spend money on your brand, understandably, they want this experience for them to be as comfortable as possible.
Apart from the above stats, this study also indicated that consumers predominantly expect multilingual customer support from brands or at least a localized chatbot to answer their basic inquiries.
The Growing Need for Multilingual Chatbots
For a business, having multilingual conversational AI brings certain benefits (apart from reaching a wider audience):
- You stand out from the competition. Having this live chat brings a 73% satisfaction rate; there are not too many businesses offering this option to foreign customers.
- You reduce costs. It is obvious that making your business go international costs millions of dollars. You can save a considerable part of this budget by introducing a multilingual chatbot that will handle a huge chunk of your customer service work.
- You can save some time. Apart from saving you a lot of money, multilingual chatbots also save you time, as they handle a lot of customer inquiries in a foreign language, while your customer support is still going through language training or you’re still in the process of hiring customer service speaking this language.
Before we get to practical advice, let’s answer the question that is probably torturing you the most right now.
Also Read: How Conversational AI adds a competitive edge to your Enterprise |
Why Localize and Not Translate?
While localization and translation are often compared, these are two separate services that differ in their nature.
Translation is a more general service that involves transforming a message from a source language to a target language. The aim is to transform the text so that the target audience could read it and perceive it as though this text was written in their native language from the start.
In its turn, localization typically involves adjusting language-specific details from a source language to a target language. Typically, professionals localize the following:
- Market adaptation of graphics and images
- Adapting content to suit the consumption habits of a foreign audience
- Design and website layout adaptation
- Making content meet local requirements (currency, date, address, and phone formats)
- Adapting technical terms to the requirements of a target language or internationalizing them
Localization is more concerned with addressing and conforming to the local regulations and requirements. It is also concerned with adapting the text to different language variations (e.g. Canadian, Australian, or American English).
The Globalization and Localization Association (GALA) is concerned with educating businesses about their localization needs and how they should approach localization to excel on the international arena.
Now, let’s dive in and discuss the best tips to localize your chatbot to conquer the international market.
1. Determine the Type of Multilingual Chatbot
In chatbot localization, the first step would be to figure out which type of chatbot that will be conversing with your foreign audience.
Even if you already have a chatbot for your English-speaking audience, you may create a separate foreign-language-speaking chatbot that performs a wider or a narrower set of tasks.
The script for your chatbot will also depend on your choice of chatbot type as well.
So, what are the types of chatbots to choose from?
Typically, AI specialists recognize two main types of conversational AI:
- Declarative (task-oriented) – serve a single purpose and perform one function. They are also called chatbots that don’t learn because they use very little Machine Learning and usually exist to respond to queries with already given answers. Such chatbots are easy to localize, as you only put in a localized target language script for the bot to follow.
- Conversational (data-driven/predictive) – use Machine Learning to not just converse with customers but also to learn from these interactions. These are virtual assistants that leverage natural language understanding and processing. These chatbots need a more instrumental approach to localization, as they follow more complex scripts.
There are also three types of chatbots based on their function:
- Menu-based chatbots – the basic type of chatbot that answers a query with a link to the FAQ page on your website. You can only localize your FAQ page and create a short localized script for the chatbot to perform simple conversations:
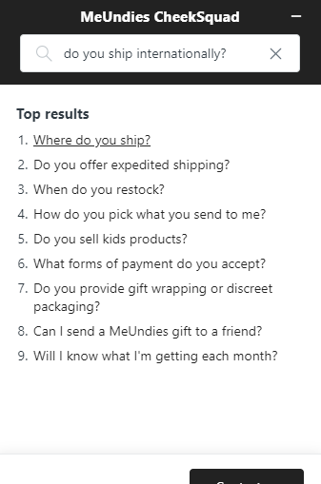
- Keyword-based chatbots – conversational AI that gives you answers based on keywords identified from your query. Such chatbots usually give more complex answers and the conversation replicates human interaction:
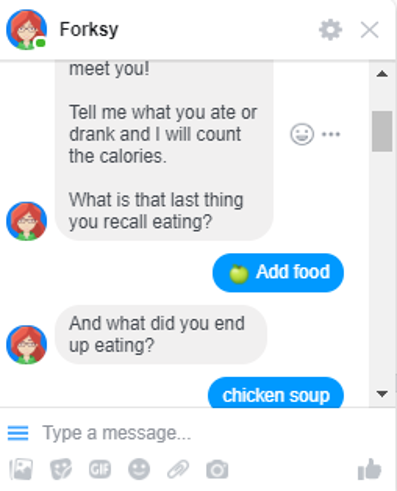 Choose the chatbot depending on the difficulty of tasks you want it to perform when conversing with your foreign audience, and move forward with preparing a script.
Choose the chatbot depending on the difficulty of tasks you want it to perform when conversing with your foreign audience, and move forward with preparing a script.
Also Read: Airlines Using Virtual Travel Assistants to Lure Customers, Capture Loyalty |
2. Get Your Source Copy Ready
So, the next localization step involves preparing a copy of the chatbot script in your native language.
Designing chatbot conversation consists of several nodes that you need to take into account before placing the script:
- User intent node – what is a user’s intent to start the conversation with a chatbot in the first place. Think from the perspective of your foreign audience right away since you will be localizing your chatbot for them.
- Entity node – what will prompt the user to input their query. It can be either their name or any other type of personal identification. Just make sure that chatbot will greet the user in accordance with the demands of their native language and culture.
After that, you can start working on the script node. Each line in the script should indicate a step that the bot will take to reply. So, when writing a script, you should take into account:
- The goal behind this script. You should always keep in mind your target foreign audience when writing this script.
- Reply limitations. When writing your script, you should remember that the answer in the language of localization may appear longer than in your source script. So keeping the answers between 60 to 90 characters in the source language is a golden middle.
- The stylistics of the replies. Keep your replies in the source language as neutral as possible to avoid misunderstandings since you address the audience that is accustomed to a different culture.
We talk a lot about getting into the mindset of your foreign audience here. “With localization, a hit-or-miss approach is not acceptable, especially when it comes to chatbots and customer support”, says Christopher Martin, a localization specialist at PickWriters. So, getting help from a professional that is native to that culture is essential to localize your chatbot successfully.
3. Highlight Details for Localization
Now, as you have your script ready, it’s time to move on to localization and highlighting the sections of the text that need special attention.
Here are several aspects to pay close attention to:
- Screen space. We already mentioned above that the localized variant in the target language may take more space than in the source language. This depends on the sentence clause structure or sentence composition, as well as on the length of words. Your typical sentence in Russian, for instance, on average is longer than a sentence in English. Thus, such sentences typically take more place on the screen and you need to pay close attention to them.
- Keyboard variations. When localizing a chatbot, it is important that it can recognize different keyboard variations, like pinyin that Chinese use to transliterate Mandarin using the Roman alphabet.
- If you are localizing a contextual chatbot that recognizes keywords from a single narrative, you need to include different abbreviations used by the target language. For instance, it’s common for Germans to abbreviate the word Adresse to Adr., or the preposition bei (near/at) to b., which should be taken into account.
Depending on the language, icons and emoji also need localization if your chatbot is using them. Sometimes, when localizing to Japanese, there is a need to localize western-type emoji (like 😉 or :-0) to Japanese-style kaomoji (^_- or ? ??).
Writing paradigms also need to be taken into account. The localization of a chatbot from English to Arabic, for instance, would mean a change from the left-to-right paradigm to the right-to-left paradigm.
Also Read: What Makes a Chatbots Platform Truly Enterprise-class |
Get In the Mindset of Your Foreign Audience
Conquering a foreign market is a great ambition. Make sure that you approach it step-by-step and with your target audience in mind.
The best way to connect with your foreign audience is by offering them customer experience which will be the most comfortable for them, i.e., in their own language. Having a chatbot that will answer all their questions and needs will ensure their allegiance to you and the smooth and successful transition of your business to the foreign market.
{{cta(‘284b444d-4361-4e0b-9d3a-1cfcb0e834f7′,’justifycenter’)}}







